Foot Health
Why should children wear barefoot shoes?
🍍 A recent research published in the British journal Nature, the study shows that: regular barefoot walking and running is good for bone and muscle health, and can regulate many functions within the body, such as increasing cortical tension in the cerebral hemispheres, which makes people feel relaxed and happy, and in addition, barefoot running is equivalent to a foot massage.
🍍 because barefoot sports, so that the bottom of the child’s feet in contact with the ground, is not only conducive to the development of the plantar skin, but also helps to improve the strength of the plantar muscles and ligaments, to promote the formation of the foot arch, to reduce and avoid the occurrence of flat feet.
Anatomy of the Foot Structure
The sole of the foot is made up of many complex bones, joints, muscles and tendons. The most important of these is the arch of the foot, which is made up of the tarsal and metatarsal bones and provides the support and flexibility that enables us to stand, walk and run.
- Bones: There are 26 bones in the foot, which together form the framework of the foot.
- Joints: There are several joints in the foot, including the ankle, metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. These joints allow the foot to move flexibly.
- Muscles and Tendons: There are many muscles and tendons in the foot that control the movement of the foot and keep the body in balance.
Most of the information in the brain about movement comes from the nerve endings in the feet, making it important to balance and coordinate the feet and the perception of the ground with the feet. This is especially important for young children learning to walk.
Bones are initially cartilage and all the components of the foot are not fully developed until the child reaches about 18 years of age. The arch also develops later in childhood, usually between the ages of 2 and 5, but sometimes later. It is not a structural part of the foot, but a muscle that needs to be utilized and exercised to develop. This is why a toddler’s foot can look very flat and can often look rolled or turned in.
All about arches, flat feet, and pronation
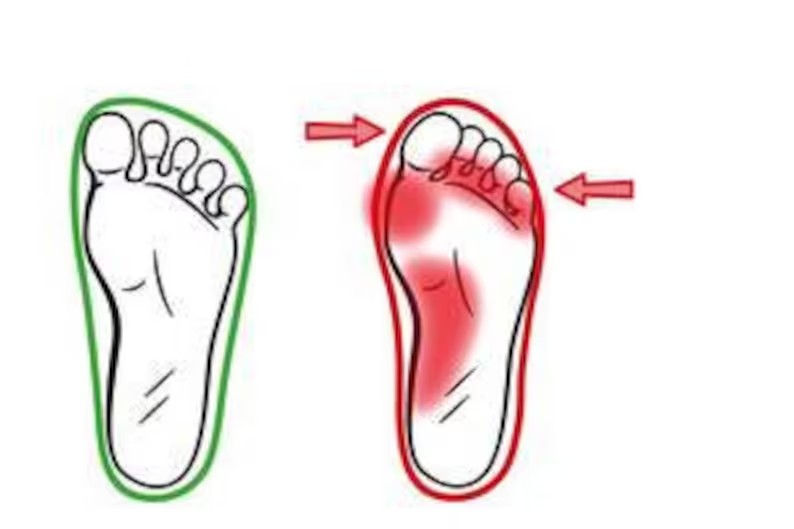
Children’s foot health is vital to growth. The arch is an important structure in the foot that helps children maintain balance while walking, running and jumping. Two common problems that affect foot health are flat feet and pronation.
Flat feet are defined as having a low arch height that causes the inside of the foot to touch the ground. Physiological flat feet are common in children and usually normalize with age. However, persistent flat feet can lead to foot pain, fatigue and gait abnormalities.
Internal rotation, in which the foot rotates excessively inward while walking or running, may lead to overloading of the inside of the foot, causing problems such as flat feet, foot pain and gait abnormalities.
To prevent and manage flat feet and internal rotation, parents can take the following steps:
1、Choose appropriate shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning.
2、Perform targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the feet.
3、Conduct regular foot examinations to understand the development of the foot arch.
4、Use arch cushions or customized insoles under professional guidance.
Learn what barefoot shoes are
Barefoot Shoes are shoes designed to mimic the sensation of walking barefoot and are intended to provide an experience as close as possible to the natural walking state. Characteristics of these shoes include the following:
Sufficient Flexibility:
Barefoot shoes usually have excellent flexibility and stretch, allowing the foot to move freely and mimicking the natural movement of being barefoot.
Thin sole design:
Barefoot shoes have very thin soles, which minimizes the isolation of the sole from the sensation of the ground and allows the wearer to better perceive the ground.
Zero or low drop: Many barefoot shoes are designed with a zero drop (i.e., the heel and forefoot are the same height) or low drop, which reduces the pressure on the feet and legs when walking and promotes a natural gait.
Loose toe:
Barefoot shoes are designed with a loose toe to provide enough room for the toes to spread naturally, which contributes to the health and comfort of the feet.
Lightweight:
Barefoot shoes are usually very lightweight, reducing the burden when walking and making the wearer feel more relaxed.
The popularity of barefoot shoes is partly due to the fact that they fit the idea of natural movement and healthy living. They are believed to help improve posture, reduce stress on the feet and legs, strengthen foot muscles, and improve balance and agility. However, due to the thin-soled design of barefoot shoes, they may not be suitable for all environments and activities, especially in situations where extra protection and support is needed.So choose the right shoe for your environment.
Flexible
Barefoot wide-toe shoes provide more room for your child’s toes to flex in all directions to reflect the natural movement of the foot, which helps to enhance strength, agility and sensory feedback for foot growth.
Wide Toe Box
Children’s feet are shaped differently than adults, in a triangular shape, requiring shoes with a larger toe area. A good toddler shoe should not just be a scaled down version of an adult shoe, but should have a spacious toe box that allows the toes to twist and spread freely. The opening of the shoe should also be wide enough for the foot to slide in easily and avoid squeezing the toes.
Light and thin
We focus on minimizing the weight of our shoes. The thickness of our different types of barefoot soles is 3-3.5mm.
Zero Drop
The heel and forefoot are at the same level, promoting natural posture, encouraging a healthy gait, and strengthening the core muscles children use to maintain balance.
Changing to Barefoot Shoes Precautions
Parents should pay attention to the following points when switching children from structured shoes to barefoot shoes:
- Gradual acclimatization: Allow your child to slowly acclimate to barefoot shoes and avoid wearing them continuously for long periods of time.
- Supervision and guidance: Make sure your child is wearing barefoot shoes correctly and instruct them in foot exercises.
- Foot protection: Choose protective shoes for your child in complex or unsafe environments.
- Foot hygiene: Teach your child to keep their feet clean and dry.
- Observe foot development: Check your child’s feet regularly and consult a professional if there are any abnormalities.
- Choosing the right barefoot shoes: Choose the right barefoot shoes according to your child’s age and type of activity.
With these precautions, your child can safely enjoy the natural walking experience of barefoot shoes.
A basic guide to shoes and foot care
- Choose shoes that fit well to ensure comfort and support.
- Choose the right shoes for the type of activity.
- Choose breathable shoes to keep your feet dry.
- Replace shoes regularly to avoid excessive wear and tear.
- Maintain foot hygiene and trim toenails regularly.
- Examine your feet regularly and consult a professional if you have any problems.
- Avoid walking barefoot to prevent injury or infection.
- Perform foot exercises to strengthen foot muscles and flexibility.
